LifeMasteryTips
We're All About Life, Mastery, And Handy Tips. Unveil Insights And Tips Spanning Learning, Business, Finance, Tech, Health Care, And Cherished Pets - Cats, Dogs, Bearded Dragons. Your Path To Mastery Begins Here.

Business
How to Hire a Content Writer & Copywriter (Tips for Hiring)
Written by
Muhammad Yaseen Khan
Business
Given the Ability to Work Fully Remote: Finding True Balance
Written by
Muhammad Yaseen Khan
Technology
The Meta Quest Pro: Virtual Reality Headset – Gorgeous Upgrade
Written by
Muhammad Yaseen Khan
Mastery
Gardening
Health
Dogs
Cats
Bearded Dragon
Bearded DragonPets
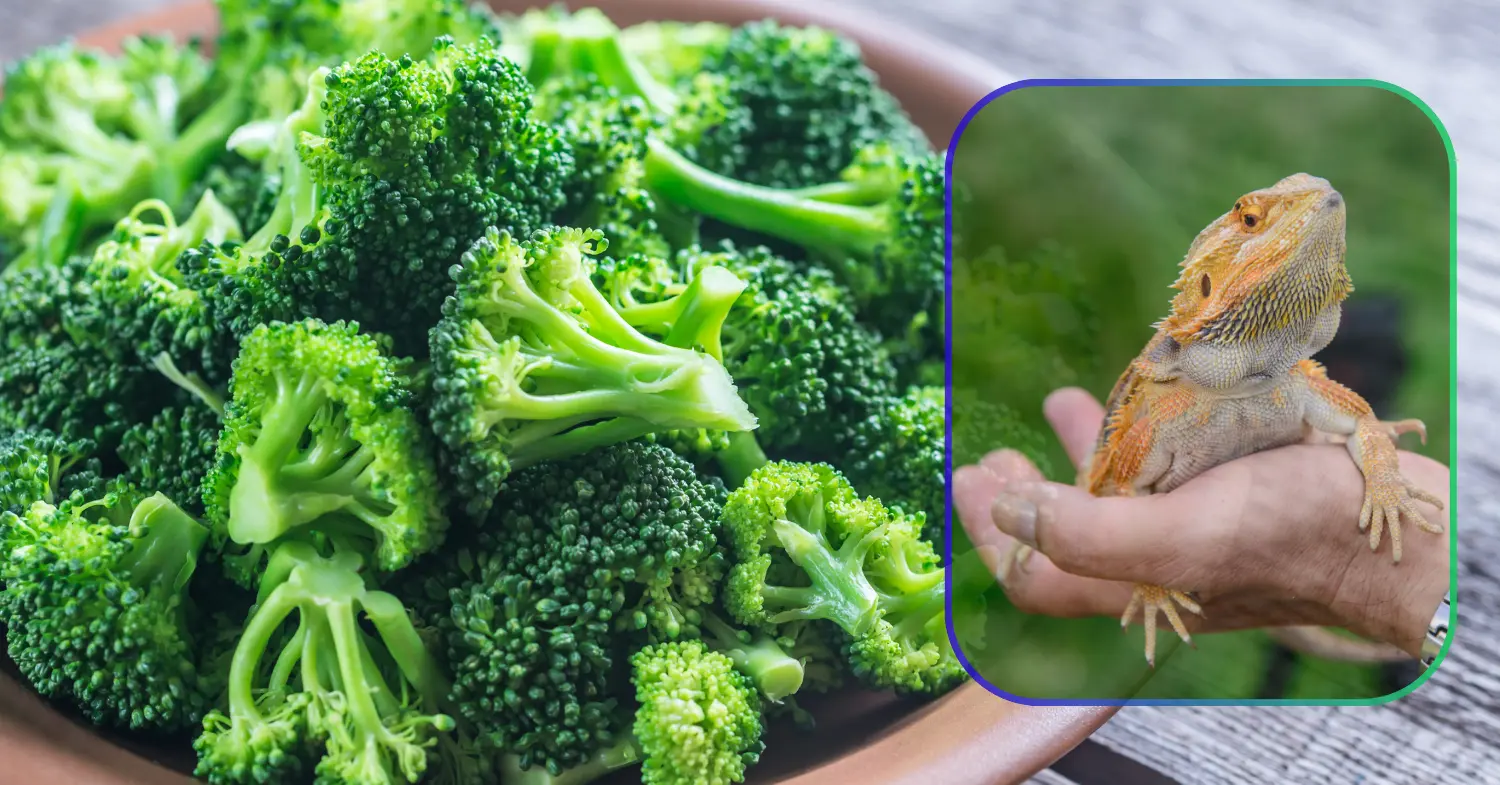
Can Bearded Dragons Eat Broccoli? Facts & Feeding Tips
Bearded DragonPets
The Fascinating World of Bearded Dragons
Bearded DragonPets
Bearded Dragon Outbreak: Salmonella and Public Health
Bearded DragonPets
Top 5 Bearded Dragon Clothes: Adding Style and Comfort to Your Pet
Bearded DragonPets
Cute Bearded Dragon Drawing
Bearded DragonPets